Overview
The article addresses the key differences between asynchronous (async) and synchronous (sync) learning, focusing on their timing, engagement, and flexibility. It highlights that synchronous learning fosters immediate interaction and collaboration, while asynchronous learning offers flexibility and self-paced engagement, with both methods having distinct advantages that cater to diverse educational preferences and needs.
Introduction
The landscape of education is evolving rapidly, shaped by the increasing demand for flexible learning solutions that cater to diverse needs.
Synchronous and asynchronous learning represent two distinct approaches, each with its own set of advantages and challenges.
- Synchronous learning thrives on real-time interaction, creating opportunities for immediate feedback and collaborative engagement.
- Asynchronous learning offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing students to learn at their own pace.
This article explores the key differences between these two methods, delves into their respective benefits, and provides insights into how educators and organizations can make informed decisions about which approach best suits their goals.
As the online education sector continues to grow, understanding these modalities becomes crucial for maximizing student engagement and enhancing educational outcomes.
Understanding Synchronous and Asynchronous Learning
Synchronous education encompasses educational interactions that occur in real-time, facilitating simultaneous engagement between instructors and participants. This approach often includes live lectures, webinars, and virtual classrooms, which enable immediate feedback and foster active participation. A key advantage of synchronous education is its ability to create a dynamic environment, as highlighted by academic advisor Vivian Jones, who noted,
With online instruction, engagement is just different.
Additionally, a case study titled "Teachers' Perspectives on Online Learning" examines Saudi EFL teachers' views, uncovering valuable insights into the advantages and disadvantages of both synchronous and alternative methods in educational environments. Conversely, non-traditional education provides the flexibility for students to access course materials and finish assignments at their own pace, without the need for real-time interaction. This method typically includes pre-recorded lectures, discussion forums, and self-paced courses, accommodating a variety of educational styles and personal schedules.
Recent trends indicate a significant growth in online education, with the number of undergraduates enrolled exclusively in online courses surging from 2.4 million to 7 million between 2019 and 2020. This shift underscores the increasing importance of async vs sync methods in contemporary education. Additionally, companies that utilize per employee that is over 200% higher, showcasing the economic advantages of investing in such educational strategies.
This trend not only highlights the effectiveness of the educational methods but also emphasizes their relevance in the context of tech startups.
Key Differences Between Async and Sync Learning
The crucial differences between education methods can be summarized in the context of async vs sync, focusing on three key factors:
- Timing
- Engagement
- Flexibility
Synchronous education requires all participants to engage simultaneously, fostering immediate interaction and collaboration, which is essential for activities such as discussions and group projects. This format often cultivates a structured environment that can enhance motivation and accountability among learners.
In contrast, asynchronous education provides significant flexibility, allowing individuals to engage with content according to their own schedules. This adaptability is particularly beneficial for those balancing various commitments, enabling self-directed study and personalized pacing. Research indicates that a balanced approach, integrating both async vs sync methods, can cater to diverse educational preferences and enhance overall engagement.
Significantly, a case study titled 'Balancing Asynchronous and Synchronous Education' demonstrates how blended educational models and flipped classrooms can enhance participant engagement by merging the advantages of both formats. Furthermore, statistics indicate that for each one-point rise in , there is an enhancement of approximately 0.6% in final exam performance, emphasizing the effectiveness of customized educational approaches. As pointed out by Picciano, the use of hybrid course formats, which combine both online and face-to-face instruction, can provide students with the advantages of both async vs sync learning experiences.
The choice between these modalities, particularly async vs sync, can profoundly influence the effectiveness of educational experiences, making it imperative for educators and institutions to consider individual preferences and needs when designing instructional strategies.
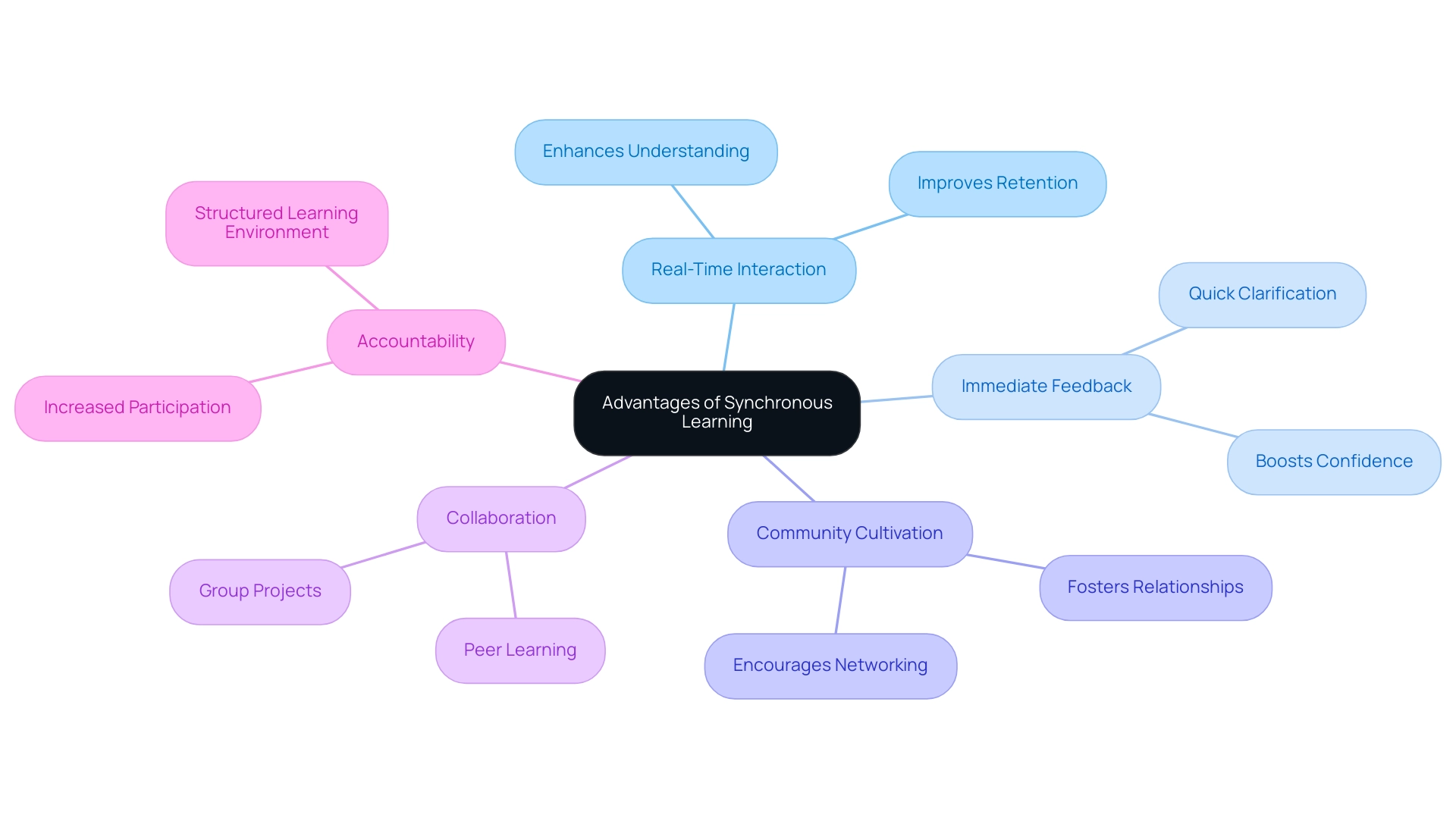
Advantages of Synchronous Learning
When comparing async vs sync education, synchronous education presents a multitude of advantages, such as real-time interaction, immediate feedback, and the cultivation of a community among participants. This approach encourages collaboration and discussion, significantly enhancing both understanding and retention of material when considering async vs sync methods. Moreover, a well-organized educational setting that highlights the differences between async vs sync methods assists individuals in upholding accountability and participation throughout their academic journey.
In 2024, studies suggest that satisfaction rates among pupils in synchronous educational settings are notably high, especially when considering the benefits of async vs sync methods, with many participants valuing the immediacy of feedback and the dynamic nature of real-time discussions. Significantly, 49% of individuals globally have participated in online education, emphasizing the importance of these approaches. For tech startups, understanding the differences between async vs sync learning methodologies can be particularly beneficial, as it not only facilitates networking opportunities but also promotes collaborative projects, essential for establishing a robust brand identity and fostering a sense of community.
Practical examples, like those from recent case studies, demonstrate how these synchronous exchanges relate to the concept of async vs sync, boosting learner engagement and ultimately resulting in better educational outcomes and a stronger bond among participants. As Ashley, an individual in Ohio State’s online Bachelor of Science in Health Sciences program, remarked, ' have been invaluable in advancing my career in health care, allowing me to connect with peers and instructors instantly.
Advantages of Asynchronous Learning
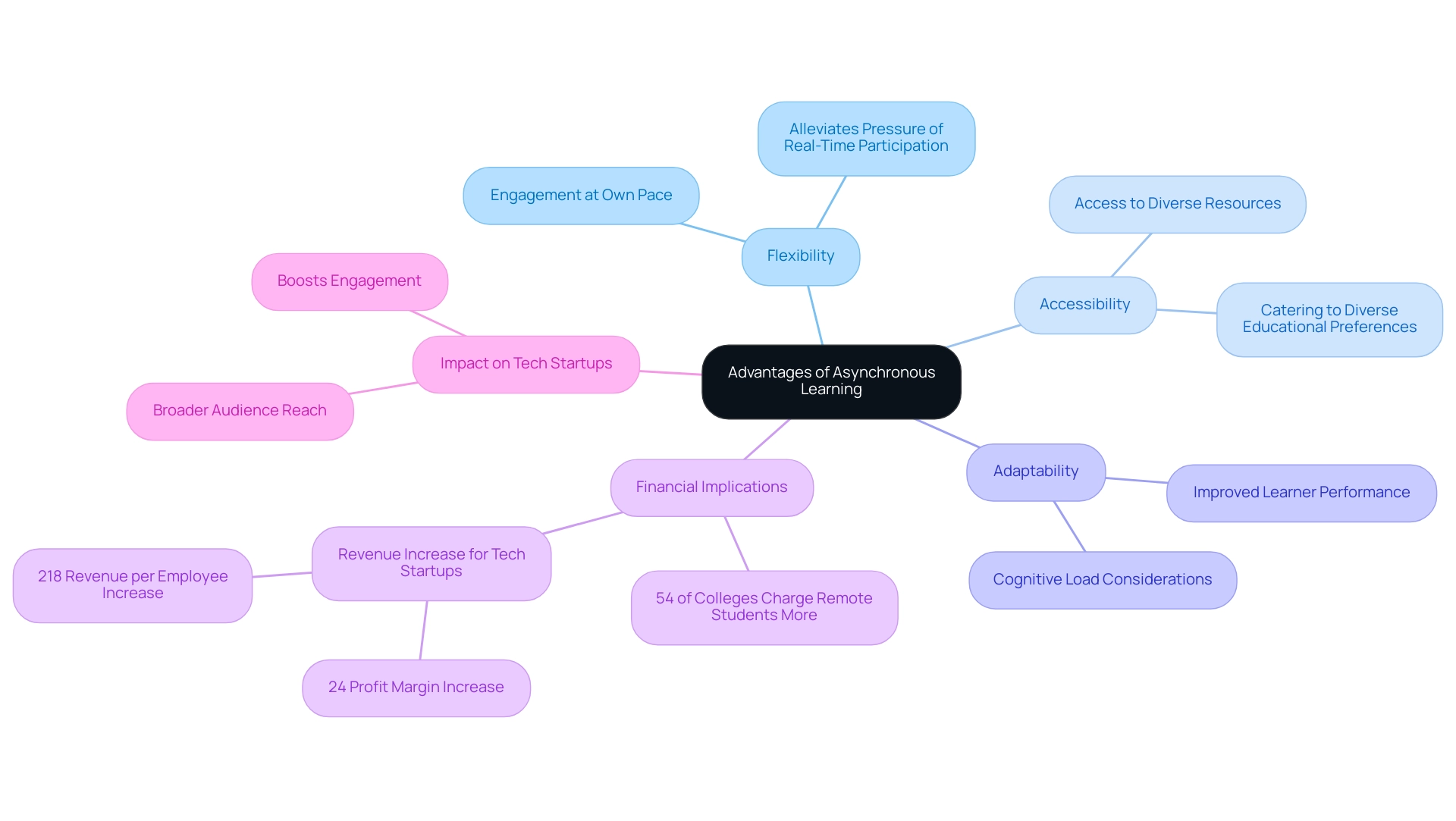
Asynchronous education presents numerous advantages, especially in the context of async vs sync, particularly in terms of flexibility, accessibility, and adaptability to diverse styles of acquisition. This educational format allows learners to engage with materials at their own pace, fostering deeper understanding and reflection. For individuals juggling various commitments—such as work and family responsibilities—this approach highlights the benefits of async vs sync attendance, alleviating the pressure associated with real-time participation and ultimately improving educational outcomes.
A case study titled 'Benefits of Online Learning' highlights how this model transforms knowledge acquisition and skill development, demonstrating its effectiveness in various educational settings. Recent studies suggest that in 2024, flexible education continues to prosper, with notable advancements in learner performance associated with its adaptable framework. Notably, 54% of colleges charge remote students more than in-person students, which underscores the financial implications of adopting asynchronous education.
For tech startups, embracing this educational format not only broadens audience reach but also boosts engagement by facilitating connections with a diverse learner base. Quotes from industry experts further emphasize this point:
As if wasn’t impressive enough, revenue per employee increased dramatically after the introduction of online education as well, by an average of 218% <—a testament to the effectiveness of this model in driving educational and business success. Moreover, the capacity to cater to diverse educational preferences positions flexible education as an essential element in the approach for enhancing online presence and building a strong brand in the competitive technology environment, particularly when evaluating async vs sync options.
Educators should also consider cognitive load when designing online curricula to enhance the educational experience and effectiveness of asynchronous programs.
Making the Right Choice: Sync vs Async Learning
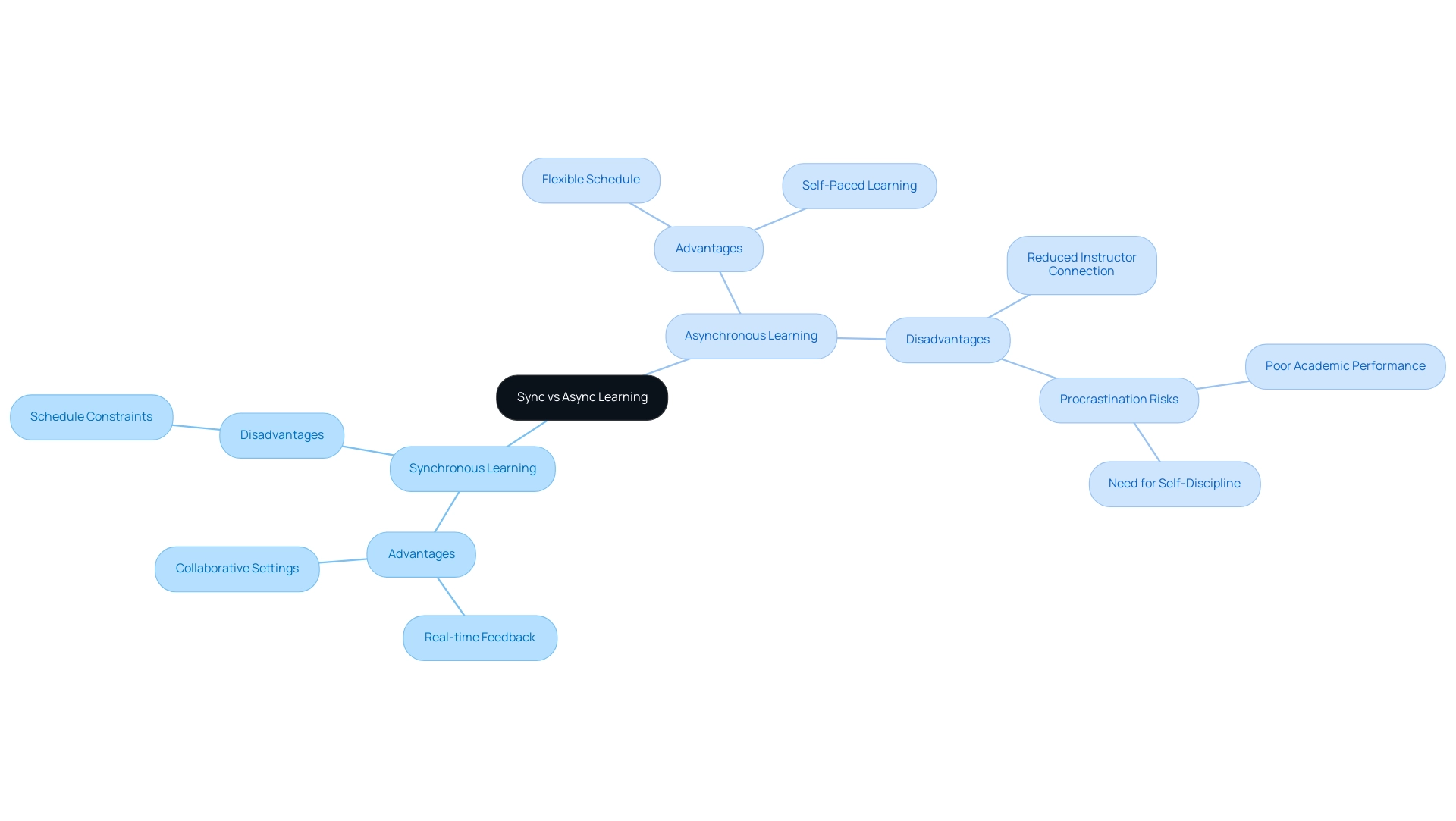
When determining the most effective educational method, the comparison of async vs sync requires considering several critical factors. These encompass personal education preferences, schedule flexibility, and the desired degree of engagement. For example, when considering async vs sync education, synchronous education is often preferred by those who thrive in collaborative settings and benefit from real-time feedback.
This method encourages prompt engagement and dialogue, making it ideal for learners who appreciate direct communication with instructors and peers. On the other hand, non-traditional education offers a choice between async vs sync learning, catering to individuals who require flexibility and wish to study at their own pace, allowing them to manage their time more effectively. However, it is essential for organizations to consider the potential drawbacks of non-traditional education, such as reduced instructor connection and limited peer interaction.
A case study highlights these challenges, noting that individuals with higher procrastination levels within asynchronous environments often perform poorly academically, underscoring the necessity for self-discipline and effective time management. This is especially pertinent considering the demographic context of participants in a recent study, which included 16 male and 24 female students aged 18–30, indicating diverse preferences for acquiring knowledge. Furthermore, the findings suggest that the results may not be generalizable to other institutions due to specific conditions at Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
As , Content Marketing Manager at Influencity, observes,
Combining both approaches ensures a balanced educational experience that accommodates diverse styles and preferences.
Therefore, organizations should assess their audience's unique preferences and needs to determine which method aligns best with their branding and engagement strategies, ultimately ensuring a more impactful learning experience.
Conclusion
The discussion of synchronous and asynchronous learning highlights the distinct advantages and challenges each approach presents. Synchronous learning fosters real-time interaction, enhancing collaboration and immediate feedback, which can significantly improve student engagement and retention. This model is particularly beneficial for those who thrive in structured environments with direct access to instructors and peers. Conversely, asynchronous learning offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing students to tailor their educational experience to fit their personal schedules, making it an ideal choice for those balancing multiple commitments.
Both methods play a crucial role in the evolving landscape of education. The growth of online education underscores the necessity for educators and organizations to consider a blended approach, integrating the strengths of both synchronous and asynchronous learning. This hybrid model not only accommodates diverse learning styles but also maximizes engagement and educational outcomes, ultimately leading to improved performance.
In conclusion, the choice between synchronous and asynchronous learning should be guided by the specific needs and preferences of learners. By understanding the unique characteristics of each method, educators and institutions can make informed decisions that enhance the learning experience. As the educational sector continues to adapt, embracing a combination of these approaches will be essential for fostering a dynamic and effective learning environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is synchronous education?
Synchronous education involves real-time educational interactions, allowing simultaneous engagement between instructors and participants through live lectures, webinars, and virtual classrooms. This format promotes immediate feedback and active participation.
What are the advantages of synchronous education?
A key advantage of synchronous education is its ability to create a dynamic learning environment that fosters immediate interaction and collaboration, enhancing motivation and accountability among learners.
How does asynchronous education differ from synchronous education?
Asynchronous education allows students to access course materials and complete assignments at their own pace without real-time interaction. It typically includes pre-recorded lectures, discussion forums, and self-paced courses, offering greater flexibility for learners.
What recent trends have been observed in online education?
There has been significant growth in online education, with the number of undergraduates enrolled exclusively in online courses increasing from 2.4 million to 7 million between 2019 and 2020. This trend highlights the rising importance of both asynchronous and synchronous methods in education.
What are the three key factors that differentiate synchronous and asynchronous education?
The three key factors are timing, engagement, and flexibility. Synchronous education requires simultaneous participation, while asynchronous education allows for flexible engagement according to individual schedules.
What does research suggest about integrating both synchronous and asynchronous methods?
Research indicates that a balanced approach that integrates both synchronous and asynchronous methods can cater to diverse educational preferences and enhance overall engagement among learners.
What insights does the case study 'Balancing Asynchronous and Synchronous Education' provide?
The case study demonstrates that blended educational models and flipped classrooms can enhance participant engagement by combining the advantages of both synchronous and asynchronous formats.
How can the choice between synchronous and asynchronous modalities impact education?
The choice between these modalities can significantly influence the effectiveness of educational experiences, making it essential for educators and institutions to consider individual preferences and needs when designing instructional strategies.




