Overview
In the world of software development, many founders face the daunting challenge of creating efficient systems. Programming, which involves crafting software through compiled languages like C++ and Java, is often seen as the solution for high-performance applications. However, it can feel overwhelming, especially when considering the intricacies of performance and resource management.
On the other hand, scripting offers a more nurturing approach, automating tasks with interpreted languages such as JavaScript and Python, focusing on flexibility and ease of modification. This distinction is vital, as programming is suited for complex applications, while scripting shines in automating repetitive tasks and enhancing existing software.
By understanding these complementary roles, tech startup founders can navigate their development journey with greater confidence and support, knowing that both programming and scripting have unique strengths to offer.
Introduction
In the world of software development, many developers face a common challenge: the distinction between programming and scripting often becomes unclear. This confusion can lead to frustration, particularly when navigating complex projects. Programming is generally linked to building robust software systems through compiled languages, whereas scripting is about automating tasks using interpreted languages.
As the demand for efficient and flexible solutions continues to rise, developers may wonder how they can effectively harness both programming and scripting to enhance their productivity. What are the critical differences that could impact their project outcomes?
This article seeks to explore these fundamental contrasts and applications, offering insights that empower developers to make informed choices in their tech journeys. Together, we can navigate these complexities and find the right balance for your development needs.
Define Programming and Scripting: Core Concepts
Programming can often feel overwhelming, especially for those navigating the complexities of . The process involves through an organized set of instructions written in languages like C++, Java, and Python. These dialects are typically compiled, meaning the code is transformed into machine code before execution. This approach allows for enhanced performance and resource management. On the other hand, scripting involves writing code that automates tasks or manages software programs. Languages such as JavaScript, Python, and Ruby are usually interpreted, permitting direct execution without a compilation phase. This distinction highlights the focus of , indicating that programming is aimed at developing independent software, whereas scripting emphasizes automation and .
As we look ahead to 2025, it's anticipated that around 36.4% of developers will embrace coding systems, reflecting a growing need for . Experts stress that while programming is crucial for , these tools also play a significant role in . For instance, C++ is widely used for , like real-time simulations and financial systems, while Java remains a cornerstone for enterprise solutions due to its reliability and scalability. As Adam Ipsen insightfully remarks, "Like Python, Java has been a consistent entry on our list, remaining in #2 since 2022—always the bridesmaid, never the bride." This perspective beautifully illustrates the complementary relationship between programming vs scripting in today's software development landscape. Together, they offer a nurturing approach to tackling the challenges faced by developers, fostering a .
Contrast Programming and Scripting: Key Differences
Understanding the essential differences between can be a challenge, especially for those navigating the complexities of . The execution models and intended uses of these systems often create a divide that can feel overwhelming. For instance, programming languages like C++ and C# are usually compiled, offering execution speeds that can be up to a thousand times faster than interpreted systems. This speed makes them ideal for large-scale projects where performance is critical. However, this can also lead to frustration when flexibility is needed. On the other hand, provide that flexibility and ease of modification, which can be a breath of fresh air for quick development and automation tasks.
In the world of , programming is predominantly utilized for creating complex systems where performance and resource management are paramount. Many tech founders turn to C++ for . Yet, in their own right, often automating repetitive tasks, writing test scripts, or enhancing existing applications. Take JavaScript, for example; it is widely embraced for adding interactivity to web pages, while Python is a favorite for data analysis and automation.
When it comes to , the interplay between front-end and back-end technologies vividly illustrates these contrasts. Front-end development relies on HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to craft engaging user interfaces, while back-end programming employs languages like Python, Ruby, and PHP for server-side logic and database management. This division underscores the vital roles both programming and markup systems play in the development ecosystem, each serving distinct yet complementary purposes.
Moreover, the portability of interpreted systems allows code to run on various platforms without modification, highlighting their advantages in specific scenarios. Additionally, Just-In-Time (JIT) compilation represents a hybrid approach that enhances the performance of both programming and scripting systems by compiling frequently used code during execution. This balance of speed and adaptability can be a game changer for startups seeking efficiency.
As you navigate these choices, remember that you are not alone. RNO1 is here to between , ensuring that your is as smooth as possible.
Explore Applications: Where Programming and Scripting Shine
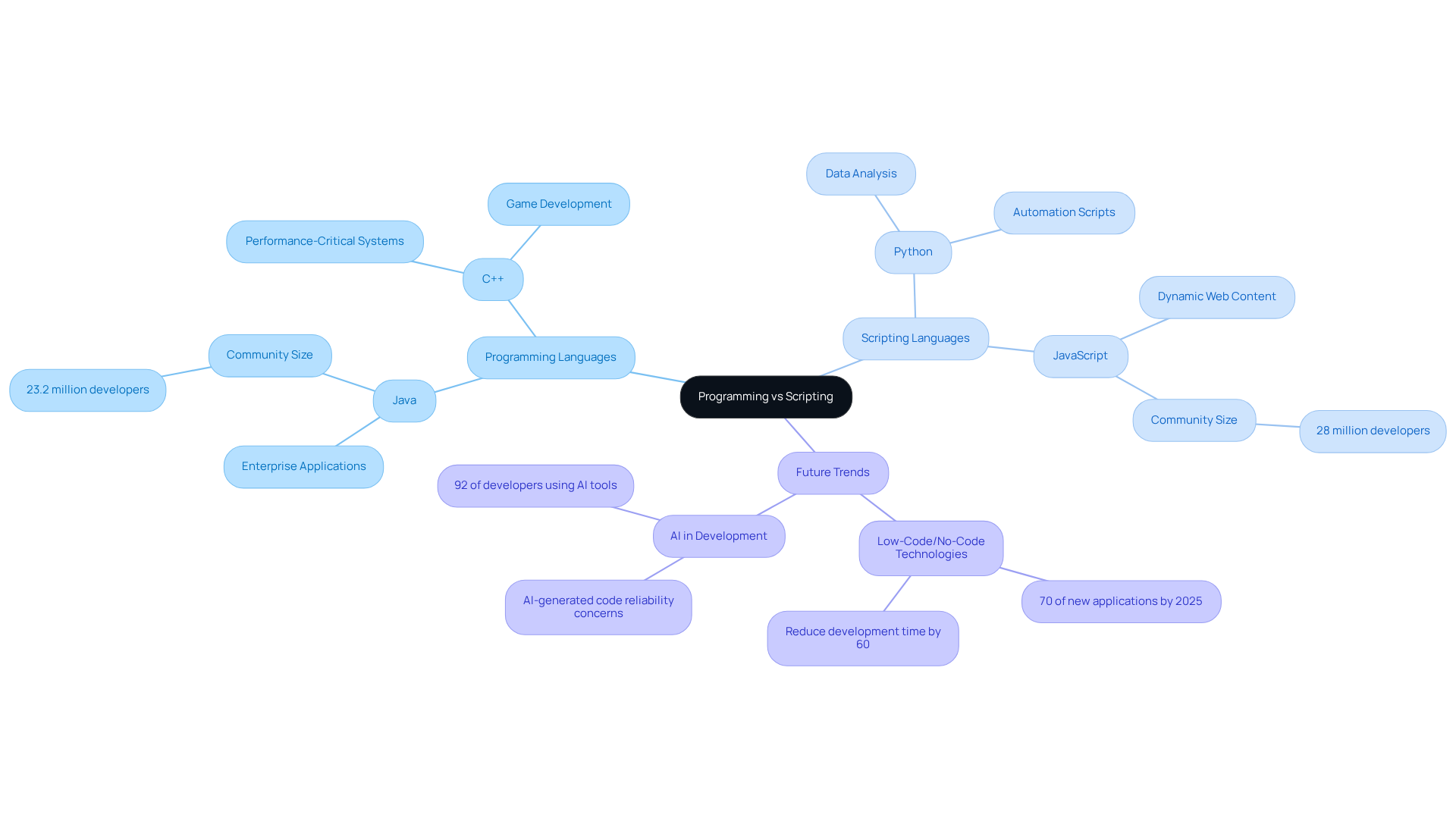
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, many developers face the daunting challenge of creating . Whether it's operating systems, enterprise software, or complex algorithms, the pressure can feel overwhelming. Languages like Java and C++ often serve as reliable allies in the debate of , providing the strength needed for . Yet, when considering programming vs scripting, shine in their ability to automate tasks, enhance web platforms, and manage system operations seamlessly.
For instance, Python is a go-to for data analysis and automation scripts, while JavaScript is indispensable for crafting . As we look ahead to 2025, it's notable that still rely on JavaScript, underscoring its vital role in web creation. Moreover, with around 28 million developers in its community, JavaScript's significance is evident. TypeScript is also emerging as a beloved choice for large-scale web projects, hinting at a promising future for JavaScript programming.
Additionally, projections indicate that by 2025, will embrace low-code/no-code technologies, reflecting a growing trend towards . Understanding these tools empowers developers to harness the strengths of each approach in programming vs scripting effectively, creating a more supportive and efficient environment for their projects. Together, we can and find solutions that resonate with our shared experiences.
Assess Pros and Cons: Evaluating Programming vs Scripting
can bring significant advantages, such as . However, many developers find themselves facing a . This can feel overwhelming, especially for those working on tight deadlines or smaller projects.
In contrast, often present a simpler learning path, allowing for . They are ideal for minor tasks and swift solutions, making them a comforting option for many. Scripting tools are frequently used to:
- Automate repetitive tasks
- Manipulate data
- Control the behavior of other programs
Yet, despite their versatility, and durability required for larger applications. For instance, while C# is adept at efficiently handling extensive data processing, Python is often the go-to for quick .
Additionally, , meaning they execute code line by line during runtime, typically requiring fewer lines of code compared to programming languages. By recognizing these strengths and weaknesses, developers can .
As John Johnson wisely noted, 'First, solve the problem. Then, write the code.' Understanding these pros and cons empowers developers to for their unique needs, fostering a supportive environment for their projects.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving world of software development, many developers face the challenge of distinguishing between programming and scripting. This understanding is vital for those striving to optimize their workflows and deliver robust solutions. Programming often revolves around crafting intricate, high-performance applications using compiled languages, while scripting focuses on automating tasks and managing processes through interpreted languages. Recognizing this difference can profoundly influence how developers approach their projects and leverage the tools available to them.
Throughout this exploration, we have delved into the key distinctions between programming and scripting, illuminating their unique strengths and applications. Languages such as C++ and Java shine in performance and scalability, making them well-suited for large-scale projects. On the other hand, scripting languages like Python and JavaScript provide flexibility and ease of use, particularly beneficial for automating repetitive tasks and enhancing web experiences. This interplay between programming and scripting fosters an environment ripe for innovation, empowering developers to choose the right tools tailored to their specific needs.
As we look to the future, the industry is increasingly moving towards automation and simplified development processes. It is crucial to understand both programming and scripting, as this knowledge can significantly enhance a developer's ability to navigate challenges effectively. Embracing the unique advantages of each approach not only equips developers to tackle obstacles with confidence but also positions them to thrive in a rapidly changing technological landscape. By harnessing the strengths of both programming and scripting, developers can create solutions that are efficient and aligned with the future of software development, fostering a sense of community and support among their peers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is programming?
Programming involves creating software systems through an organized set of instructions written in languages like C++, Java, and Python. It typically requires compiling the code into machine code before execution, which enhances performance and resource management.
What is scripting?
Scripting refers to writing code that automates tasks or manages software programs. Languages such as JavaScript, Python, and Ruby are usually interpreted, allowing for direct execution without a compilation phase.
What is the main difference between programming and scripting?
The main difference is that programming is focused on developing independent software applications, while scripting emphasizes automation and task management within existing software environments.
What is the expected trend in developer coding systems by 2025?
It is anticipated that around 36.4% of developers will embrace coding systems by 2025, reflecting a growing need for automation in software creation.
Why is programming important for software development?
Programming is crucial for building resilient software, as it allows developers to create robust applications that meet high-performance requirements.
How do programming and scripting complement each other?
Programming and scripting together foster a supportive environment for innovation in software development, helping to tackle challenges faced by developers and enhancing efficiency in workflows.
What are some examples of programming languages and their uses?
C++ is widely used for high-performance requirements like real-time simulations and financial systems, while Java is a cornerstone for enterprise solutions due to its reliability and scalability.




