Overview
Many startups face the challenge of having a website that doesn't meet user needs. Bad websites often exhibit:
- Poor usability
- Confusing navigation
- Slow loading times
- Unappealing aesthetics
This can lead to a frustrating user experience, which not only affects user satisfaction but can also harm your brand's reputation. It's disheartening to know that these design flaws can significantly decrease engagement and conversion rates. In fact, evidence shows that 88% of users are unlikely to revisit a poorly designed site. This statistic highlights the pressing need for effective web design, which is crucial for your business success. By investing in a thoughtfully designed website, you can create a welcoming space that resonates with your audience and fosters lasting connections. Remember, a well-designed website is not just an asset; it's a vital part of your journey towards success.
Introduction
A website serves as a digital storefront, but what happens when it fails to meet user expectations? Bad websites, characterized by poor usability, confusing navigation, and slow loading times, not only frustrate visitors but can deeply impact a brand's reputation and profitability. This situation can feel overwhelming, especially in an increasingly competitive digital landscape.
Understanding the implications of these design flaws is crucial for businesses aiming to enhance their online presence. It’s important to recognize that these challenges can be transformed into opportunities for improvement and user engagement.
How can we, as a community, support each other in navigating these hurdles together?
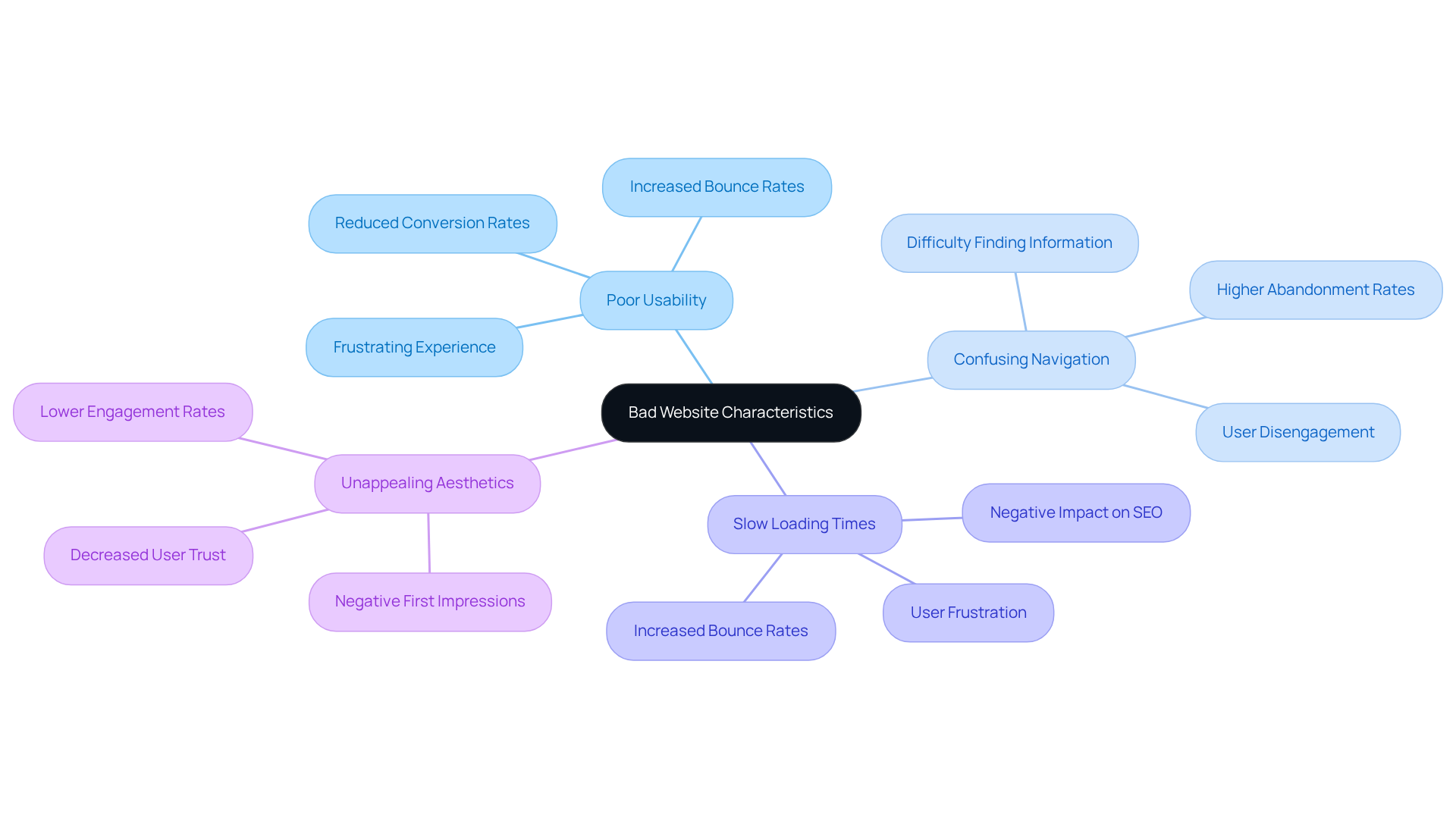
Define Bad Website: Core Characteristics and Implications
A poorly designed online platform is often categorized as one of the bad websites, presenting several challenges such as:
- Poor usability
- Confusing navigation
- Slow loading times
- Unappealing aesthetics
These issues can create a frustrating experience for visitors, leading them to leave bad websites. Think about it—bad websites, overwhelmed with excessive advertisements or lacking mobile responsiveness, fail to meet user expectations, which can deeply affect a brand's reputation. In fact, studies reveal that 32% of consumers would stop engaging with a brand after just one negative experience. This statistic underscores the financial risks tied to insufficient planning.
The implications of bad websites extend far beyond mere aesthetics; they can significantly impact a company's bottom line by reducing conversion rates and increasing bounce rates. At RNO1, we understand these challenges all too well. We believe that a is essential for overcoming them. By prioritizing aesthetics in every interaction, we aim to transform digital experiences and enhance brand trustworthiness. Our goal is to ensure that companies not only meet but exceed user expectations.
Recognizing these core characteristics is vital for businesses striving to build a strong online presence. We invite you to reflect on your own experiences with online platforms. Together, we can navigate these challenges and create a digital landscape that is not only functional but also inviting and engaging.
Identify Key Design Flaws: Common Issues in Bad Websites
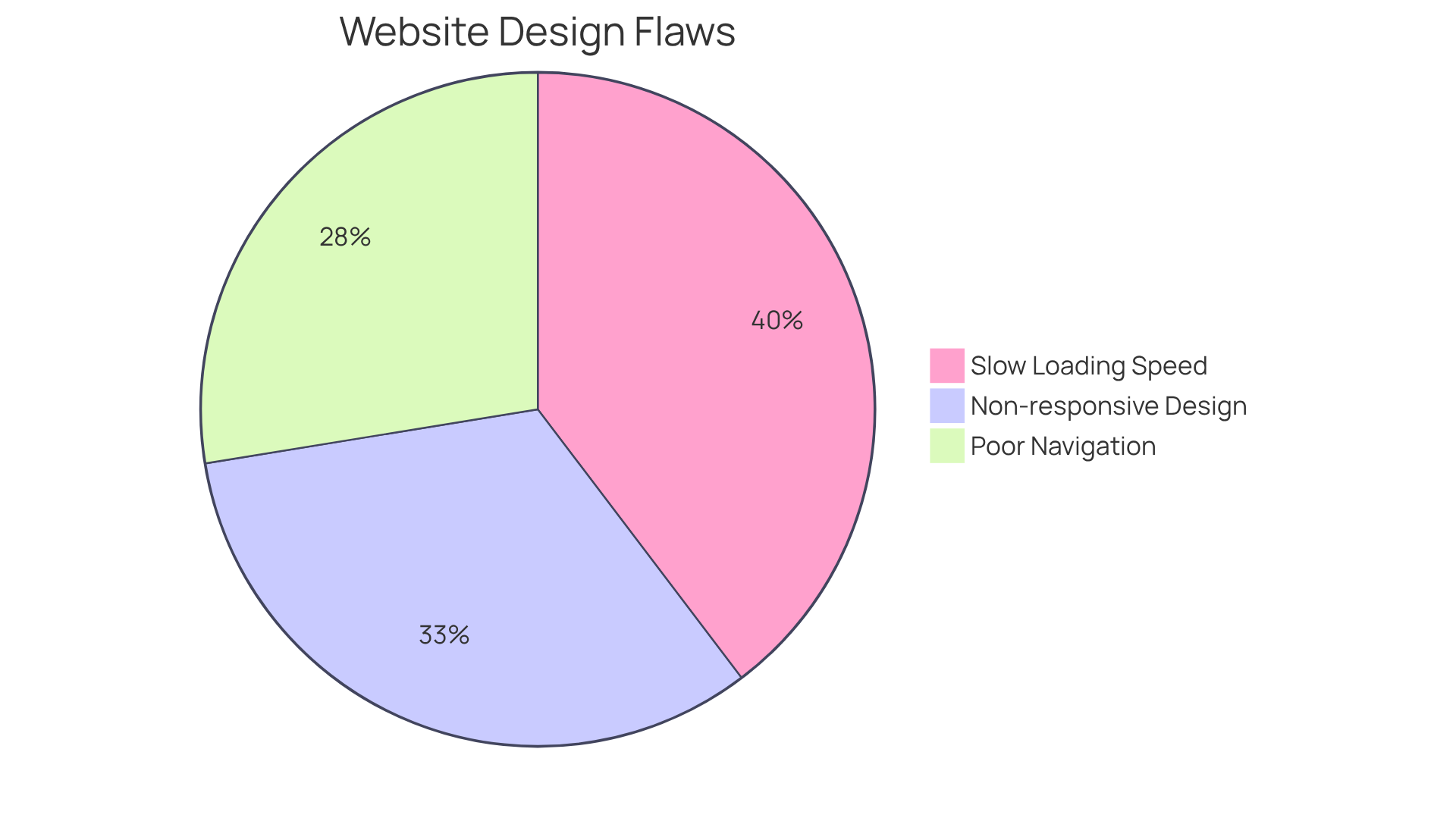
Frequent construction flaws in bad websites present a real challenge for many. Complicated navigation, slow loading speeds, and inadequate mobile optimization are characteristics of bad websites that can leave visitors feeling frustrated and lost. Imagine trying to find essential information on a site with overly complex menus—it can be bewildering.
In fact, a significant 73.1% of web designers believe that non-responsive design is a primary reason for visitor abandonment, while 61.5% point to bad websites with poor navigation as a leading cause for individuals leaving a site. The impact of slow loading times compounds this issue; for each second a site takes to load, the likelihood of visitors bouncing increases by a staggering 123%. Moreover, ecommerce sites that load in just one second enjoy conversion rates that are three times greater. With 88.5% of users citing slow site speed as a major reason for leaving, it’s evident that performance is crucial for retaining visitors.
Another significant flaw is the lack of mobile optimization. With accounting for approximately 78% of retail and eCommerce website traffic, bad websites that do not adapt to various screen sizes risk alienating a substantial portion of their audience. Studies reveal that 60% of shoppers find usability essential for online purchasing, and mobile-friendly layouts can lead to a remarkable 75% increase in return visits. A compelling case is illustrated by EcoFoil, which saw an 86% increase in purchases after modifying their layout and design.
By addressing these common challenges, organizations can significantly enhance user experience and improve their overall online effectiveness, fostering a more supportive and engaging environment for all users.
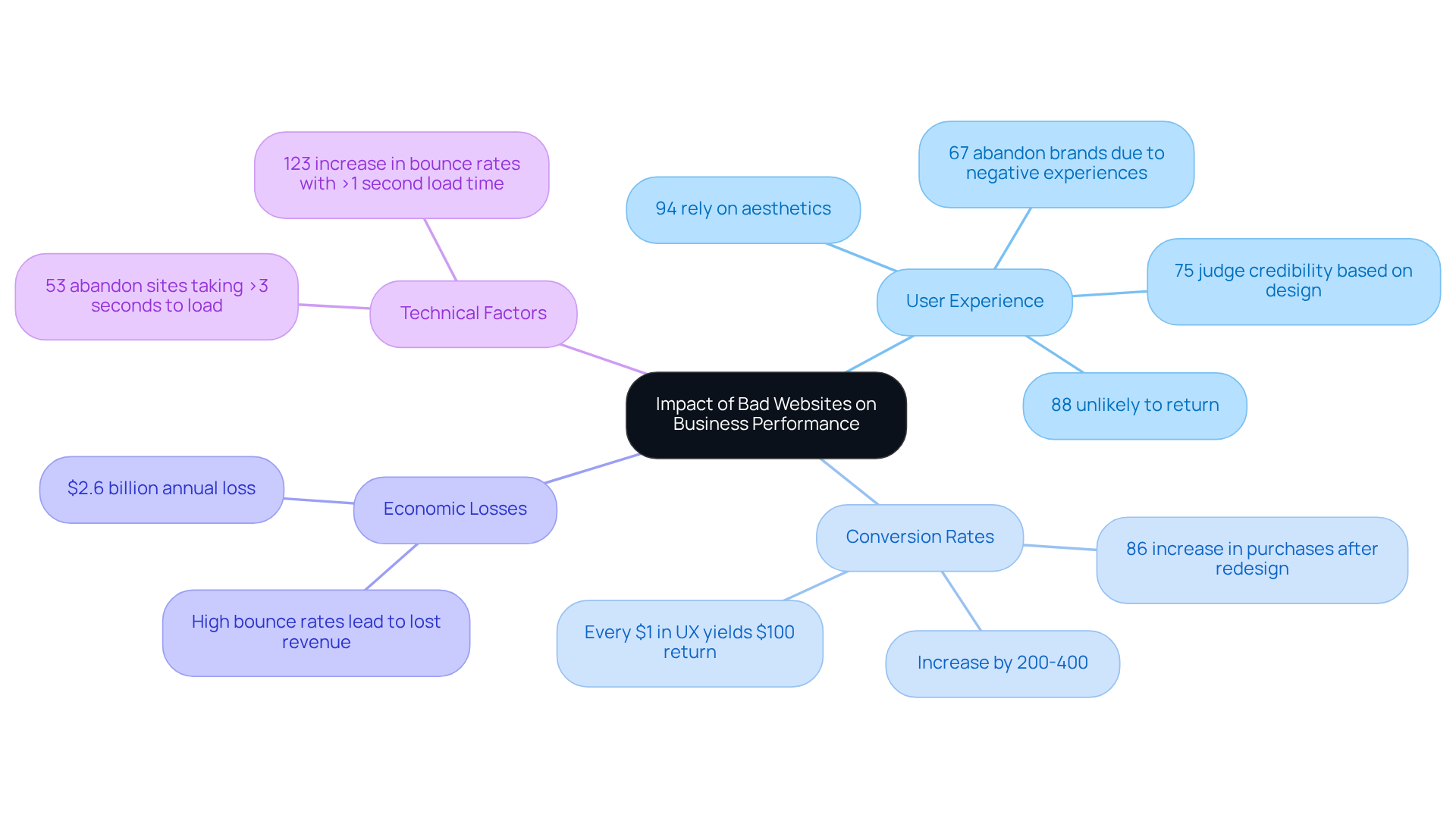
The Impact of Bad Websites on Business Performance
The effect of a badly constructed online platform on business performance is considerable and complex. Many of us have faced the frustration of navigating bad websites that simply don’t meet our needs. Research shows that 88% of users are unlikely to revisit a website after such an encounter, which underscores the necessity of investing in quality web aesthetics. Negative experiences can lead to decreased engagement and lower conversion rates; studies indicate that enhancing user experience can increase conversion rates by as much as 200%. Moreover, a strong UX strategy can push conversion rates up to 400%, showcasing the potential for substantial improvements through thoughtful design. It’s important to remember that a well-structured online platform not only improves user satisfaction but also fosters trust, a crucial element for boosting sales.
Conversely, bad websites can adversely affect search engine rankings, making it increasingly difficult for potential clients to discover your business online. For instance, businesses that have revamped their online platforms often report significant advancements in conversion rates; one case study revealed an 86% rise in purchases after a homepage overhaul that prioritized user-friendly navigation. This illustrates that investing in effective web development is not merely an aesthetic choice but a strategic business decision that can enhance visibility and profitability. Unfortunately, businesses are facing a staggering $2.6 billion annual loss due to inadequate customer experience, highlighting the economic consequences of neglecting site aesthetics.
Ultimately, the layout of an online platform plays a vital role in shaping visitor perceptions and experiences. With 94% of initial perceptions relying on aesthetics, it’s essential for companies to prioritize to retain clients and cultivate long-term loyalty. Additionally, we must consider technical factors like page loading times; 53% of individuals abandon mobile sites that take more than three seconds to load. This further emphasizes the importance of a well-optimized platform. Let’s work together to ensure that your online presence not only meets but exceeds the expectations of your users.
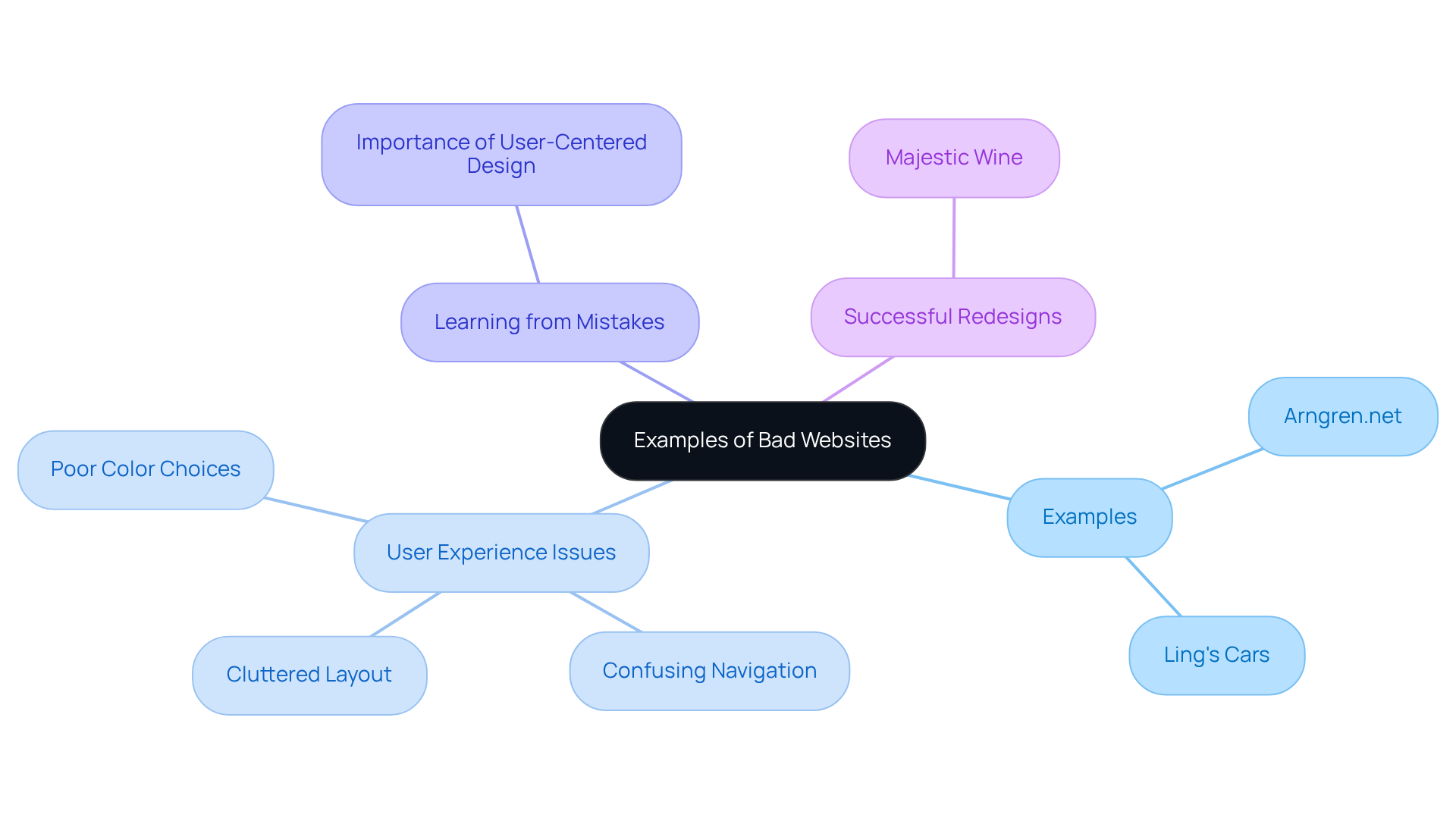
Examples of Bad Websites: Learning from Mistakes
Many instances of bad websites highlight the challenges of ineffective web creation, significantly impacting the experience of visitors. Websites like Arngren.net and Ling's Cars are examples of bad websites that illustrate , often leaving visitors feeling overwhelmed by excessive animations, poor color choices, and dense text. Such structural flaws can lead to user frustration, with studies indicating that 38% of users are likely to abandon bad websites if they find the layout unattractive.
Learning from these mistakes is vital for businesses looking to enhance their online presence. For instance, Ling's Cars is often cited as one of the bad websites because its disorganized layout detracts from usability and engagement. In contrast, successful redesigns, like those seen with Majestic Wine, showcase the power of simplifying layouts and improving messaging, leading to a remarkable 201% increase in inquiry form submissions.
Web development specialists emphasize the importance of avoiding common pitfalls, noting that bad websites often feature overloaded pages and complex navigation, which are significant contributors to user abandonment. By reflecting on these flawed examples, companies can gain valuable insights into creating more effective, user-friendly online experiences that foster engagement and drive conversions. RNO1's collaboration with Figure highlights how focusing on user-centered design can transform digital experiences, ensuring that companies not only navigate typical challenges but also thrive in a competitive landscape.
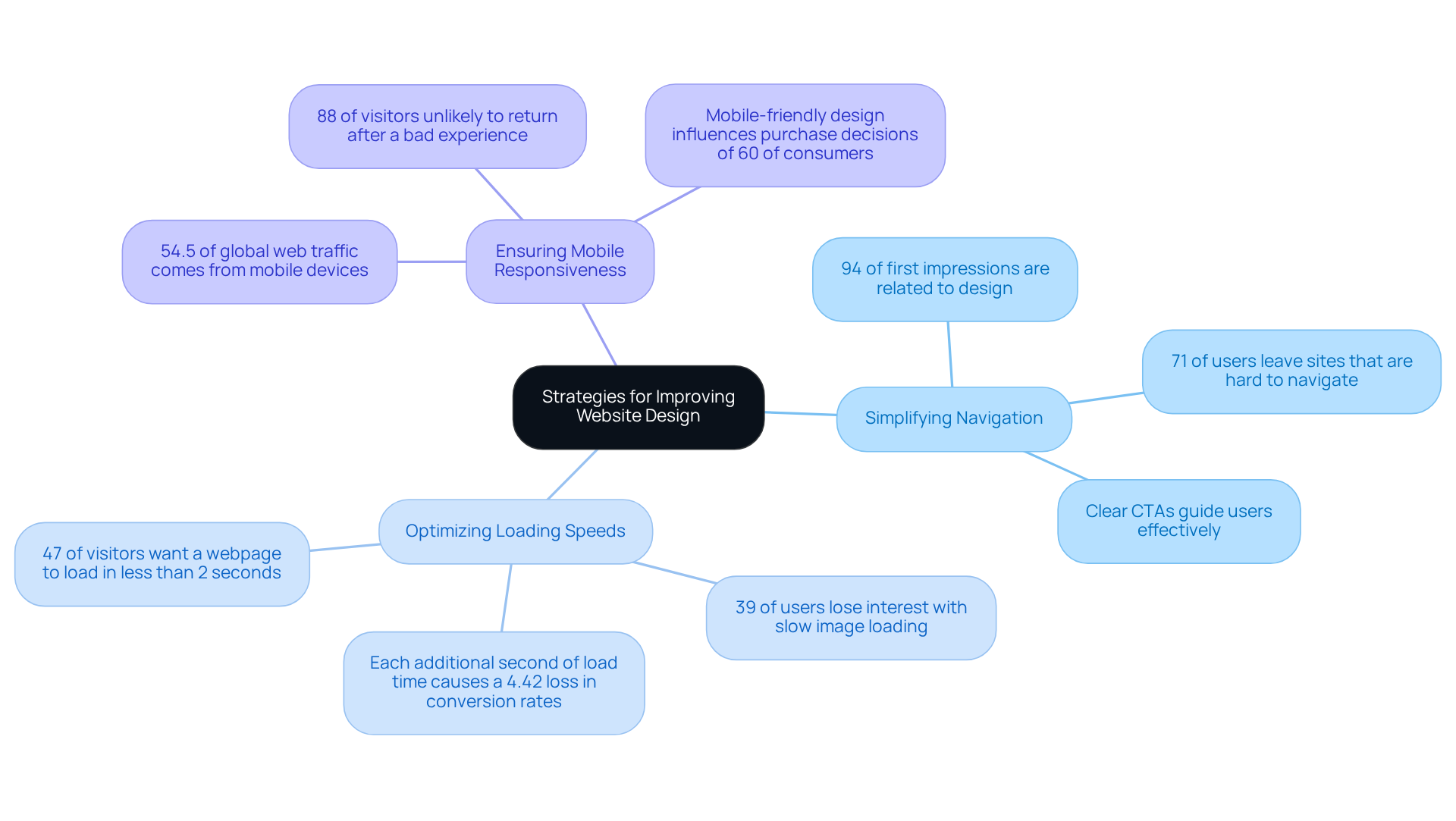
Strategies for Improving Website Design
To improve website aesthetics and prevent the creation of bad websites, companies face the challenge of prioritizing user-focused principles. This includes:
- Simplifying navigation
- Optimizing loading speeds
- Ensuring mobile responsiveness
It's concerning to note that 88% of visitors are unlikely to return to bad websites after a negative experience, underscoring the importance of an effective layout. Conducting participant testing becomes essential, as it allows businesses to gather valuable feedback on actual interactions, paving the way for iterative enhancements. For instance, a revamp of the Greenventory app led to a significant boost in customer satisfaction and engagement metrics, highlighting the positive impact of intentional UX planning.
At RNO1, we are deeply committed to being design-focused across every touchpoint. Our goal is to ensure that our solutions not only fulfill functional needs but also create a strong visual impact. We embrace methodologies such as user journey mapping and iterative prototyping to enhance user experience. Studies reveal that 94% of initial perceptions are tied to a design's aesthetics, making it crucial for companies to invest in an attractive interface. Additionally, ensuring that online platforms are mobile-friendly is vital, especially since more than 54.5% of global web traffic comes from mobile devices. By prioritizing these strategies, businesses can avoid bad websites and craft those that are not only visually appealing but also perform effectively, ultimately driving better results and increasing conversion rates. We invite you to and thoughts as we navigate this journey together.
Conclusion
In today’s digital landscape, a well-constructed online presence is not just beneficial; it is essential for any business striving to thrive. Bad websites—those marked by poor usability, confusing navigation, and slow loading times—can alienate potential customers and tarnish a brand's reputation. It’s crucial to recognize and address these core issues if we want to enhance user satisfaction and drive conversions.
Consider the significant impact that design flaws can have on user experience and overall business performance. Alarming statistics reveal how easily users abandon sites that fail to meet their expectations, leading to financial repercussions for companies that neglect web aesthetics. It becomes clear that a well-designed website is not merely an option; it is a necessity. Successful redesigns demonstrate how prioritizing user-centered design can lead to increased engagement and sales.
The importance of investing in effective website design cannot be overstated. Businesses must strive to create online platforms that are visually appealing, functional, and user-friendly. By adopting best practices—like simplifying navigation and optimizing for mobile devices—organizations can transform their digital experiences and foster long-term customer loyalty. Embracing these strategies will not only mitigate the risks associated with bad websites but also pave the way for greater success in an increasingly competitive online marketplace. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; together, we can create a digital environment that welcomes and retains customers, nurturing your business's growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the core characteristics of a bad website?
Core characteristics of a bad website include poor usability, confusing navigation, slow loading times, and unappealing aesthetics.
How do bad websites affect user experience?
Bad websites create a frustrating experience for visitors, leading them to leave the site due to issues like excessive advertisements or lack of mobile responsiveness.
What is the impact of a negative experience on consumer engagement?
Studies show that 32% of consumers would stop engaging with a brand after just one negative experience, highlighting the financial risks associated with poor website design.
How can bad websites influence a company's bottom line?
Bad websites can reduce conversion rates and increase bounce rates, significantly impacting a company's financial performance.
What design flaws are commonly found in bad websites?
Common design flaws include complicated navigation, slow loading speeds, and inadequate mobile optimization.
What percentage of web designers believe non-responsive design leads to visitor abandonment?
Approximately 73.1% of web designers believe that non-responsive design is a primary reason for visitor abandonment.
How does slow loading speed affect visitor retention?
For each second a site takes to load, the likelihood of visitors bouncing increases by 123%. Slow site speed is cited by 88.5% of users as a major reason for leaving.
Why is mobile optimization important for websites?
Mobile devices account for about 78% of retail and eCommerce website traffic. Bad websites that are not mobile-friendly risk alienating a significant portion of their audience.
What are the benefits of having a mobile-friendly layout?
Mobile-friendly layouts can lead to a 75% increase in return visits, and usability is essential for 60% of shoppers when making online purchases.
Can improving website design lead to increased sales?
Yes, for example, EcoFoil saw an 86% increase in purchases after modifying their layout and design, demonstrating the positive impact of good design on sales.




